When did birds first appear? This question has intrigued scientists and nature enthusiasts for centuries. Birds, with their incredible diversity and unique adaptations, hold the key to understanding the evolution of life on Earth. In this article, we will explore the origins of birds, their evolutionary journey, and the fascinating discoveries that have shaped our understanding of these remarkable creatures.
Birds have always been a symbol of freedom and grace. Their ability to fly and their vibrant plumage make them one of the most captivating groups of animals on the planet. But when exactly did these creatures first appear? By delving into the fossil record and modern scientific research, we can piece together the story of their origins.
This article will provide an in-depth exploration of the timeline of bird evolution, the key species that contributed to their development, and the latest scientific discoveries that have reshaped our understanding. Whether you're a scientist, a bird enthusiast, or simply curious about nature, this article will offer valuable insights into the world of birds.
Read also:Does The Salt Trick For Men Really Work Unveiling The Truth Behind This Popular Trend
Table of Contents
- Evolutionary History of Birds
- Fossil Records: The Earliest Evidence of Birds
- Archaeopteryx: The Transitional Species
- Unique Characteristics of Birds
- The Evolution of Feathers
- Birds as Descendants of Theropod Dinosaurs
- The Emergence of Modern Birds
- Diversity and Adaptations of Birds
- Scientific Research on Bird Evolution
- Conclusion: Understanding the Importance of Bird Evolution
Evolutionary History of Birds
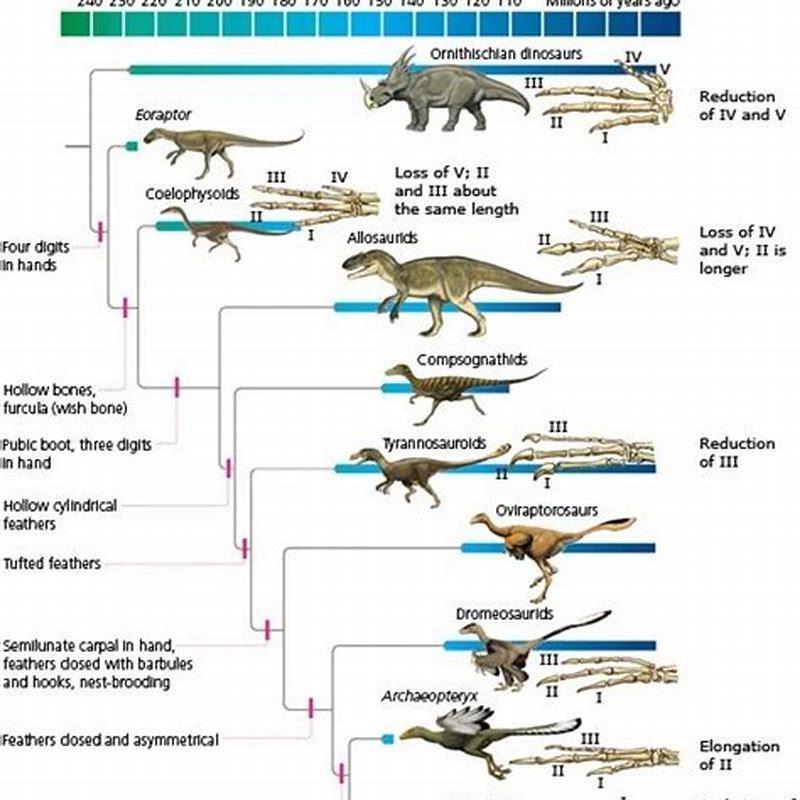
When did birds first appear? To answer this question, we must travel back in time to the Mesozoic Era, a period spanning approximately 252 to 66 million years ago. This era is often referred to as the "Age of Dinosaurs," and it was during this time that the ancestors of modern birds began to evolve.
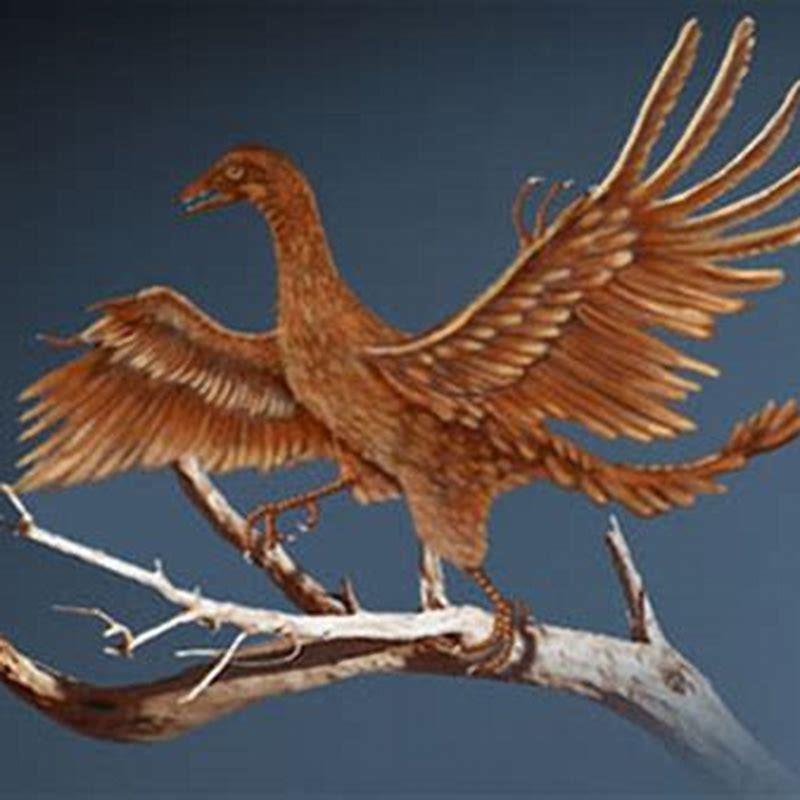
Research suggests that birds first appeared around 150 million years ago, during the Jurassic Period. This timeline is supported by fossil evidence, including the famous Archaeopteryx, which is considered one of the earliest known birds. The evolutionary journey of birds is closely linked to their theropod dinosaur ancestors, a group of bipedal carnivorous dinosaurs.
Key Milestones in Bird Evolution
- Development of feathers for insulation and flight
- Evolution of lightweight bones for efficient flight
- Adaptation of beaks for diverse feeding habits
Fossil Records: The Earliest Evidence of Birds
Fossil records provide crucial evidence for understanding when birds first appeared. The discovery of Archaeopteryx in the late 19th century was a groundbreaking moment in paleontology. These fossils, found in the Solnhofen limestone deposits in Germany, revealed a creature with both avian and reptilian features.
Archaeopteryx, which lived around 150 million years ago, had feathers similar to modern birds but also retained characteristics of its dinosaur ancestors, such as teeth and a long bony tail. This combination of traits makes it a key transitional species in the evolution of birds.
Significance of Fossil Discoveries
- Providing evidence of the evolutionary link between birds and dinosaurs
- Shedding light on the development of flight and other avian traits
- Supporting the theory of gradual evolution through natural selection
Archaeopteryx: The Transitional Species
Archaeopteryx is often referred to as the "first bird" due to its unique combination of avian and reptilian features. This species serves as a critical link between non-avian dinosaurs and modern birds. Its discovery has been instrumental in shaping our understanding of bird evolution.
Key characteristics of Archaeopteryx include:
Read also:Pining For Kim Tailblazer A Comprehensive Guide To The Iconic Fashion Trend
- Feathers with a modern structure, indicating the ability to glide or fly
- Clawed wings and a long bony tail, reminiscent of its dinosaur ancestors
- Teeth and a bony tail, features not found in modern birds
Studies of Archaeopteryx fossils have revealed that it likely had limited flying capabilities, suggesting that flight evolved gradually over millions of years.
Unique Characteristics of Birds
Birds possess several unique characteristics that distinguish them from other animals. These traits have evolved over millions of years, allowing birds to thrive in diverse environments and adapt to various ecological niches.
Key Characteristics of Birds
- Feathers: Used for flight, insulation, and display
- Beaks: Adapted for specific feeding habits
- Lightweight bones: Facilitating flight
- High metabolic rates: Supporting energy-intensive activities
These adaptations have enabled birds to become one of the most successful groups of animals on the planet, with over 10,000 species currently identified.
The Evolution of Feathers
Feathers are one of the most distinctive features of birds and played a crucial role in their evolutionary success. The evolution of feathers is believed to have begun in theropod dinosaurs, long before the first birds appeared.
Early feathers likely served as insulation, helping small theropods regulate their body temperature. Over time, these feathers evolved into more complex structures, eventually enabling flight. Fossils of feathered dinosaurs, such as Microraptor and Sinosauropteryx, provide evidence of this evolutionary transition.
Functions of Feathers
- Flight: Providing lift and control during flight
- Insulation: Regulating body temperature
- Display: Attracting mates and intimidating rivals
Birds as Descendants of Theropod Dinosaurs
The theory that birds are descendants of theropod dinosaurs is now widely accepted by the scientific community. This conclusion is based on a wealth of fossil evidence and comparative anatomy studies. Theropod dinosaurs, a group of bipedal carnivores, share many anatomical features with modern birds, including:
- Hollow bones
- Three-fingered hands
- A wishbone (furcula)
Studies of theropod fossils have revealed that many species had feathers, further supporting the link between dinosaurs and birds. This evolutionary relationship highlights the incredible adaptability of life on Earth.
The Emergence of Modern Birds
The emergence of modern birds occurred during the Cretaceous Period, approximately 100 million years ago. This period saw the diversification of bird species, leading to the development of the wide variety of birds we see today.
Key developments during this time include:
- The evolution of powered flight
- The adaptation of beaks for specialized diets
- The development of complex social behaviors
Modern birds, classified under the group Neornithes, are characterized by their highly efficient respiratory systems, strong flight muscles, and advanced cognitive abilities.
Diversity and Adaptations of Birds
Birds are one of the most diverse groups of vertebrates, with over 10,000 species found in virtually every habitat on Earth. This incredible diversity is a result of their ability to adapt to different environments and ecological niches.
Examples of bird adaptations include:
- Webbed feet in aquatic birds for swimming
- Long, curved beaks in hummingbirds for feeding on nectar
- Strong talons in birds of prey for capturing prey
These adaptations have allowed birds to thrive in a wide range of environments, from the icy Arctic to the scorching deserts.
Scientific Research on Bird Evolution
Ongoing scientific research continues to deepen our understanding of bird evolution. Advances in molecular biology, genetics, and paleontology have provided new insights into the evolutionary relationships between birds and their dinosaur ancestors.
Key areas of research include:
- Genetic studies of modern birds to trace their evolutionary history
- Fossil analysis to identify transitional species
- Comparative anatomy to understand the development of avian traits
These studies not only enhance our knowledge of bird evolution but also contribute to our broader understanding of evolutionary biology.
Conclusion: Understanding the Importance of Bird Evolution
When did birds first appear? The answer lies in the fascinating evolutionary journey that began over 150 million years ago. Birds, as descendants of theropod dinosaurs, represent one of the most remarkable examples of evolutionary adaptation. Their unique characteristics, such as feathers and lightweight bones, have enabled them to become one of the most successful groups of animals on the planet.
In conclusion, understanding bird evolution is crucial for appreciating the complexity and diversity of life on Earth. By studying the origins and adaptations of birds, we gain valuable insights into the processes that drive evolution and the interconnectedness of all living organisms.
Take action by exploring the world of birds further. Leave a comment below with your thoughts or questions, and don't forget to share this article with fellow bird enthusiasts. Together, we can deepen our appreciation for these incredible creatures and the natural world they inhabit.